Lithium-sulfur (Li-S) battery could become practical if 20 percent of the theoretical energy densities (2600 Wh/kg or 2800 Wh/L) can be achieved. Investigators have the ambition to reach energy density of 500 Wh/kg in the near future.
Xue-Ping Gao from Nankai University, says, “Currently, the volumetric energy density of 500 Wh/L is not satisfied. But it was already realized in commercial lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) many years ago. The low volumetric energy density is a bottleneck of practical Li-S battery.”
Intrinsically, sulfur has lower density than transition metal oxides as cathodes in LIBs. Worse, in order to improve the electrochemical performance, sulfur is usually forced to load onto various lightweight carbon hosts, leading to more lower volumetric capacity of sulfur-based composites, and undermining the volumetric energy density of Li-S battery.
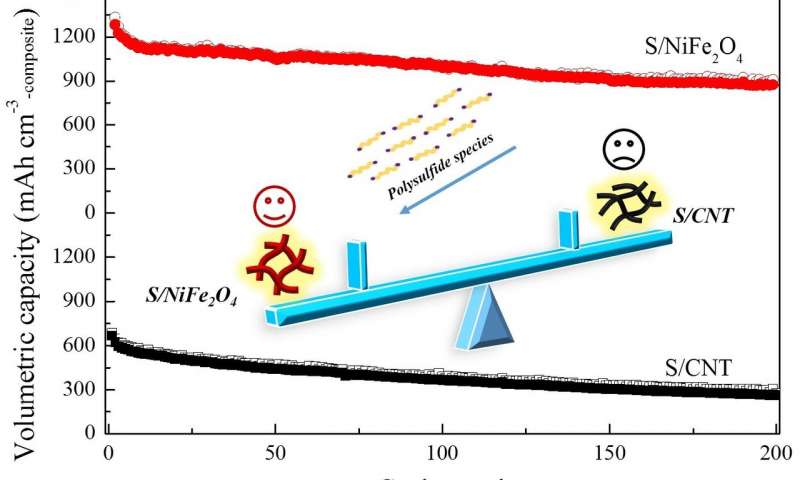
Compared with carbon materials, heavy metal oxides not only offer good adsorption ability of polysulfides to suppress the shuttle effect, but also help to obtain dense sulfur-based composites with high tap density. Gao says, “Based on this, we developed nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) porous hollow 1-D nanofibers via electrospinning technology. The as-prepared NiFe2O4 nanofibers were used here as a novel host of sulfur in order to increase the volumetric capacity of sulfur-based composites.”
Gao details their experiment, “Firstly, the polysulfide adsorption test reveals the strong chemisorption towards soluble polysulfides by NiFe2O4.” Both the stable adsorption geometry and adsorption energy of Li2S8 on (111) plane of NiFe2O4 are confirmed by Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculation as compared with carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
As a result, the S/NiFe2O4 composite delivers an initial discharge capacity of 963.6 mAh/g, and good cycle stability. “Furthermore, the S/NiFe2O4 composite shows nearly 2 times higher superior volumetric capacity than S/CNT composite. It comes as no surprise that the S/NiFe2O4 composite has a much larger tap density than the S/CNT composite,” he said.
In addition, other metal ferrites MFe2O4 (M = Co, Mg, Zn) have also been investigated as polar hosts of sulfur, and the results confirm the superiority of metal ferrites in fabricating sulfur-based composites with high gravimetric/volumetric capacities for the potential application of Li-S batteries with high gravimetric/volumetric energy density.
