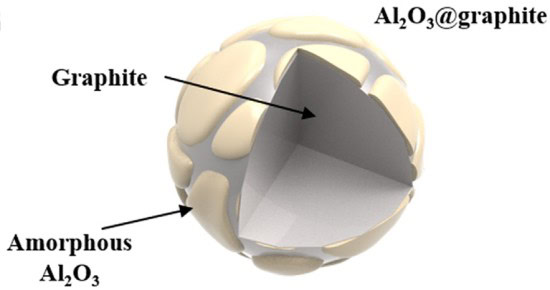
A team of researchers from Hanyang University in South Korea has demonstrated that surface modification of graphite using amorphous Al2O3 is an efficient way to improve the fast charging capability of graphite anode materials for lithium ion batteries.
In a paper in the Journal of Power Sources, the researchers report that surface-engineered graphite with 1 wt% Al2O3 exhibits a reversible capacity of about 337.1 mAh g−1, even at a high rate of 4000 mA g−1, corresponding to 97.2% of the capacity obtained at a current density of 100 mA g−1.
Along with rapid expansion of electric vehicle (EV) markets have come greater demands on lithium ion batteries (LIBs). These face various technical challenges for EV applications in terms of energy density, power density, reliability and safety. In particular, fast charging capability is a highly valued feature because it shortens the charging time of LIBs. Unfortunately, current lithium ion battery technology cannot fully meet the desired charging rates for EVs. To resolve this LIB technical drawback, it is of utmost importance to find suitable battery materials that can be operated at extremely fast charging rates without sacrificing the electrochemical performance and safety of the battery. To attain this goal, various strategies have been implemented to improve the charging capability of LIBs with varying levels of success.
… It is well recognized that wettability between the electrolyte and the electrode plays a crucial role in determining the electrochemical performance of LIBs.
… In this work, amorphous Al2O3 was introduced to improve the fast charging capability of graphite anode material. It is well known that amorphous Al2O3coatings can significantly improve wettability of the battery materials, such as graphite, and separators. We anticipated that an amorphous Al2O3 coating would promote electrolyte penetration over the entire surface area of the graphite electrode, thereby enhancing the fast charging capability of the graphite anode material.—Kim et al.
Full cell tests adopting LiCoO2 cathodes and Al2O3-coated graphite anodes confirmed that the introduction of amorphous Al2O3 can improve the fast charging capability of graphite anode materials.
Wettability tests and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis revealed that this fast charging improvement results from the increased electrolyte wettability on the graphite that is induced by the Al2O3 layer on its surface.
Our proposed material concept, i.e., introduction of a shell layer to improve the electrolyte wettability of a graphite electrode, may be a practical way of improving the fast charging capability of graphite as an anode material for use in high-power LIBs.—Kim et al.
