The automotive industry is regarded as one of the more cutting edge sectors that often leads the way for new technologies such as artificial intelligence and autonomous systems. Blockchain is being seen as one such technology, and it is unsurprising that the industry is immersing itself in this new space.
Car manufacturers have been quietly picking up on the blockchain phenomenon, trying to figure out different ways in which they can utilize the immutable ledger to their different needs.
For example, on June 11, IOTA and Volkswagen demonstrated a proof-of-concept that uses IOTA’s Tangle system for autonomous cars. This is just one application of blockchain technology in the automotive industry.
So, while it is not all self driving cars and space-age applications, there are already the likes of BMW who are using blockchain to track the cobalt they use in manufacturing to ensure ethical mining.
The scope of applications for blockchain can range from something as simple as BMW’s logistics, to Volkswagen’s autonomous car, and everything in between, as the automotive industry continues to push for more use-cases of the technology.
Entering the space
There is a long list of ways in which the automotive industry can leverage blockchain, and some of those uses are starting to be snapped up and attempted by the bigger manufacturers.
Porsche, BMW and Mercedes made news earlier this year as they began putting the blockchain to the test. BMW has its cobalt ledger, Mercedes introduced its safe driving program that rewards drivers in crypto and Porsche with its blockchain apps.
But there are others following close on their heels as they try and corner the blockchain market for the automobile industry. In fact, it is not just blockchain for cars, some well known manufacturers are driving the blockchain adoption alongside the likes of IBM and Bosch.
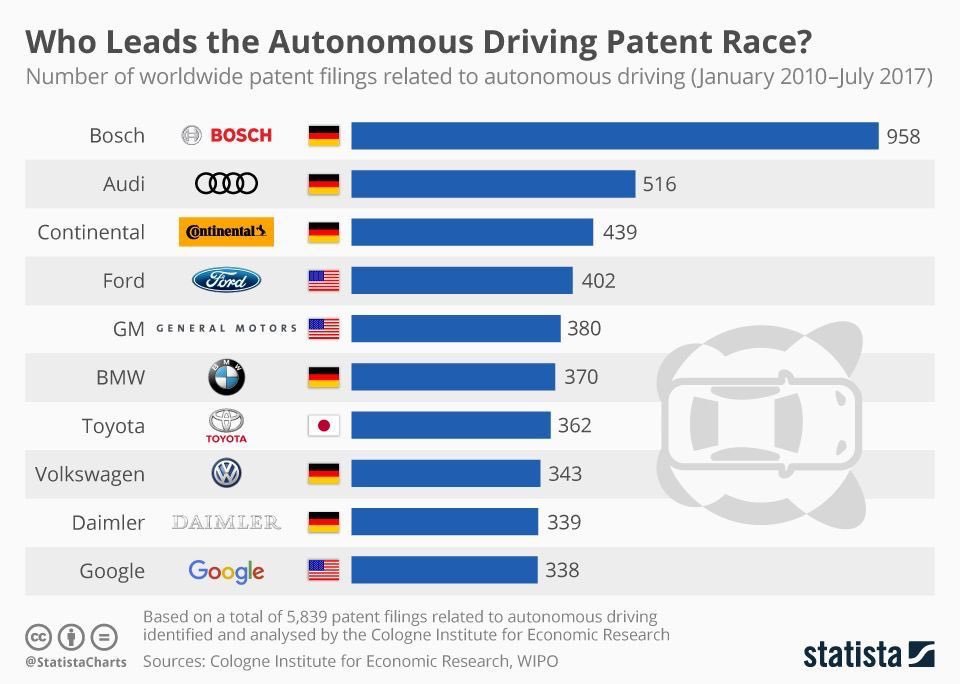
In fact, Bosch is one of the leading companies in the race for autonomous car patents. As of July 2017, Bosch held 958 patents, way ahead of second placed Audi with 512.
Furthermore, with Bosch playing an active role in blockchain promotion in its role at the Mobility Open Blockchain Initiative (MOBI), the future of automobile and blockchain technology seems more linked than ever before.
Mobility Open Blockchain Initiative
BMW, Ford, Renault and General Motors are among the 30 companies in MOBI. Founding members also include IBM, Bosch and Blockchain at Berkeley, student-run organization at UC Berkeley aimed at promoting blockchain.
MOBI was formed on May 2 when four leading automobile manufacturers launched a joint venture with the help of those additional thiry companies. The group’s mission is to speed up the adoption of blockchain and change transportation, as well as make sure the industry is on the same page with use cases ranging from autonomous payments to ride-sharing, according to MOBI’s website.
The blockchain adoption wave is making its way through a number of major sectors, from banks, corporations, even governments, but as Brian Kelly, founder and CEO of digital asset investment firm Brian Kelly Capital Management says, the automotive introduction adds a new battleground for blockchain:
“This is a tectonic shift in the tech landscape, that has the potential to disrupt the growth plans of legacy tech into the auto.”
Building use cases
The automotive use cases making the news thus far have focused predominantly around BMW, with its blockchain partnership aimed at procuring ethically sourced cobalt; Porsche and its blockchain-based apps, which include locking and unlocking the vehicle authorizing temporary access; and Daimler AG, famous for its Mercedes-Benz smart brands, who are launching their own cryptocurrency called MobiCoin to reward good drivers. These companies have started putting out tangible blockchain uses, and are now being followed by Volkswagen and IOTA with their autonomous proof-of-concept.
However, there are other instances, ranging back to 2016, of automobile companies looking to leverage the blockchain.
Toyota and blockchain supply chain management
In 2016, Toyota Financial Services joined R3CEV Consortium. In the long term, Toyota is expected to leverage blockchain technology for automotive supply chain management and connected car systems.
Toyota Financial Services is excited to join the R3CEV consortium to advance the use of distributed ledger technology in finance,” said Chris Ballinger, CEO and Global Chief Officer for Strategic Innovation at Toyota. “We believe this technology will ultimately lower costs, increase efficiency and make auto finance more transparent for our customers.”
Renault moving in the blockchain space already
Renault have been looking at the blockchain for car passports for some time now. The current method of storing information about customers and their vehicles is spread across a whole host of different information systems maintained by automakers, insurers, repair shops, and more. But Renault is looking to consolidate that information with the power of blockchain technology
Additionally, RCI Bank, owned by Renault joined the R3CEV consortium as well. RCI Bank specializes in providing automotive finance services to Renault and Nissan group companies.
“Blockchain technology, which can be likened to a ledger that is unfalsifiable and secure, is seen as a way to simplify banking infrastructure and other use cases for the benefit of the customer. It also has the potential to reinforce the security and integrity of systems while reducing processing and transaction costs, thus further benefiting banks and their customers alike,” RCI Bank said in a statement explaining the benefits of blockchain for the company.
eWallet for German car parts manufacturer
ZF Friedrichshafen AG, a German car parts maker, partnered with UBS and the innogy Innovation Hub to develop the blockchain-based Car eWallet to facilitate online payments. The eWallet is built on a blockchain ‘to ensure security.’
The use of this eWallet is said to be used as payment system that makes it possible to pay for electric car charging, for example. Additionally, the solution is said to be able to handle many other mobility-related payments, such as highway tolls, parking fees or car-sharing.
The range of uses indicates that blockchain technology can be applied in multiple ways when it comes to manufacturing of cars. The science fiction-sounding IOTA autonomous car might be the most interesting, but supply chain, vehicle tracking and smart manufacturing are already being tested and utilized more than just a proof-of-concept.
Blockchain in the automotive industry
By looking into just six areas where the automotive industry is starting to use the blockchain, one can get a sense as to how powerful this technology can be in driving the manufacturing of cars forward.
Ride sharing services
From mobility solutions, which include ride sharing services and autonomous systems, blockchain technology can put a big dent in the monopoly that companies like Uber have over shared taxi services.
Furthermore, as Uber may not be looking into blockchain technology, there is every opportunity for a decentralized system to make inroads into the model that something like Uber has set up.
Having a company that has complete control over everything that happens inside its system, and dictates its conditions for working with contractors, gives it the opportunity to abuse its power. With its current business policy, Uber is a structure that can not work without centralized power.
These are already being seen as in 2015, an Israeli company La’Zooz utilised a decentralized transportation platform, and the following year, a company called Productive Edge implemented a proof-of-concept for a smart contract taxi service.
Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing is also a big area that can help the automotive industry. Blockchain can be leveraged just like in any other level of manufacturing, but because of the complex nature of automobile building, it can drive forward things like supply chain traceability and inventory management.
Supply chain
There is also general supply chain management which is a large part of car manufacturing, and a timeous and expensive part as well. This area of manufacturing can be taken over by an effective blockchain, as can insurance claim processing for that matter.
As explained above, the passport of a car is already being tested by Renault, but the entire title transfer, vehicle tracking, retailing and leasing of cars can all be put onto the blockchain.
From the present to the future
Problems of the present are already being addressed by car manufacturers, utilizing the blockchain. They are using the technology for supply chains and car passports. But even more fascinating is the future of automobiles is getting an upgrade thanks to blockchain technology.
Volkswagen’s proof-of-concept for an autonomous car using IOTA is a window into the automobile industry of tomorrow that is being built on technology that is only just now beginning to be fully utilized and understood.
