
The diamond industry, once a symbol of timeless stability, finds itself in a state of flux as prices for natural diamonds hit multiyear lows, driven by a mix of evolving consumer preferences, geopolitical upheaval, and the meteoric rise of lab-grown diamonds (LGDs), a new study shows. ![]()
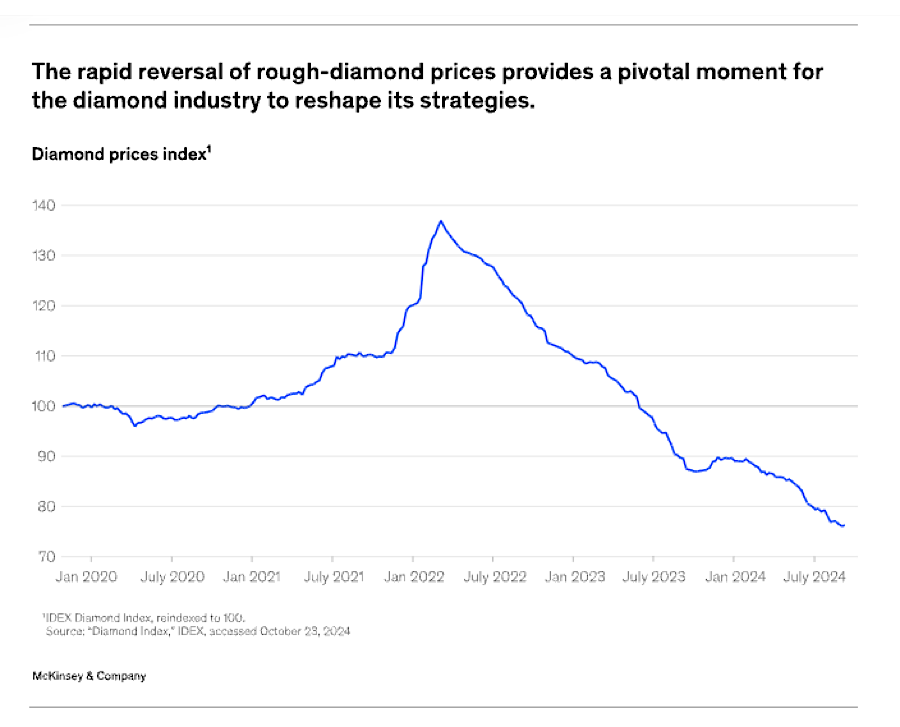
The reversal of fortunes that followed a surge during the covid-19 pandemic has left industry stakeholders grappling with how to adapt to ensure long-term sustainability, consultancy McKinsey & Company says in its latest report.
During the pandemic, diamond prices rose unexpectedly. Supply chain disruptions and the delay of weddings initially dampened sales, but many consumers stuck at home turned to diamonds as a form of self-care. This led to an unanticipated spike in demand and a sharp rise in prices.
The post-pandemic market has painted a very different picture. As traditional engagement and marriage cycles return and supply chains normalize, prices have tumbled amid changing market dynamics, McKinsey & Co. says.
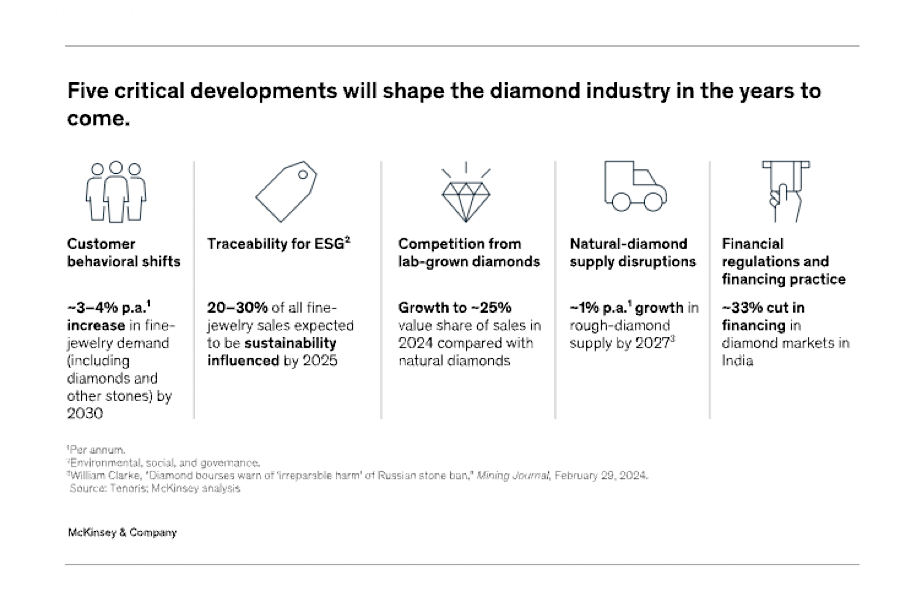
The rapid adoption of lab-grown diamonds has emerged as one of the industry’s most significant disruptors. These stones, virtually indistinguishable from natural diamonds to the naked eye, have gained popularity for their affordability and perceived ethical and environmental advantages.
Ten years ago, young customers were an important segment of the overall demand for precious stones. Today, they seek more affordable and ethical alternatives.
With prices up to 80% lower than mined diamonds, LGDs have swiftly carved out a substantial share of the market, challenging traditional producers, the report shows.
Shifting customer values
Increased awareness of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues has also driven consumers to demand greater transparency and sustainability in diamond sourcing. Many buyers now insist on proof that their diamonds were mined under fair conditions with minimal environmental impact. This shift is particularly pronounced among younger generations, who are reshaping the jewelry market with their purchasing power and values.
Generation Z is leading a wave of change, favouring ethical and customizable products over traditional offerings. Younger buyers are more likely to seek out jewelry that aligns with their values, including fair labor practices and sustainability.
Many are turning to digital platforms for their purchases, with online fine jewelry sales growing significantly. In 2021, the average online purchase of diamond jewellery in the US was $2,204, compared to $2,994 in physical stores, signalling a growing comfort with digital transactions for high-value items.
The trend of self-purchasing is another key shift. Rather than waiting for significant life events like engagements or weddings, many consumers are now buying fine jewelry for themselves.
Industry actors Beers Group and Signet Jewelers launched in October their “Worth the Wait” campaign, aimed at reigniting demand for mined diamonds from youngsters, particularly amid “zillennials”, the microgeneration born between 1993 and 1998.
Geopolitical and gov’t factors
Adding to the industry’s challenges are geopolitical tensions. Sanctions targeting Russian diamonds have disrupted the global supply chain, particularly for larger stones. Russia’s Alrosa, once the world’s top diamond producer by output, has been heavily sanctioned by the US and the European Union, creating regional dislocations.
McKinsey & Company warns that, by March 2025, these restrictions will tighten further, targeting stones of 0.5 carats and above, exacerbating supply chain issues.
The upheaval comes at a time when natural-diamond production is already constrained. Growth in supply is expected to remain sluggish, with an annual increase of just 1–2% through 2027, far below historical trends. Major mining companies are grappling with depleting resources, forcing them to shift from open-pit mining to more expensive underground operations. Companies like De Beers have invested billions to extend the life of their mines, but these efforts are costly and time-consuming.
Government intervention is also reshaping the industry. In diamond-rich regions, including Botswana, public authorities are taking larger stakes in mining operations, emphasizing the need for transparent and sustainable practices.
Despite the challenges, there are opportunities for companies willing to adapt, the consultancy says. Producers can diversify their offerings by incorporating LGDs or recycled diamonds into their portfolios. They can also emphasize the unique, intrinsic value of natural diamonds, appealing to consumers who value rarity and tradition. Investments in sustainability and digital commerce are likely to pay dividends, as consumers increasingly demand ethical and seamless shopping experiences.
The consultants conclude that by embracing innovation and aligning with shifting consumer values, the industry may find a way to shine brightly once more.
